Weight gain during breast cancer treatment is due to different reasons. In most cases, it is a consequence of hormonal disorders, metabolic alterations, depression, or a decrease in physical activity. When the weight gain is not very high or the specialist does not indicate otherwise, follow the same recommendations to maintain a balanced diet during treatment and avoid following any type of alternative or exclusionary diet that has not been prescribed as part of the oncological treatment.
WHAT DO WE RECOMMEND?
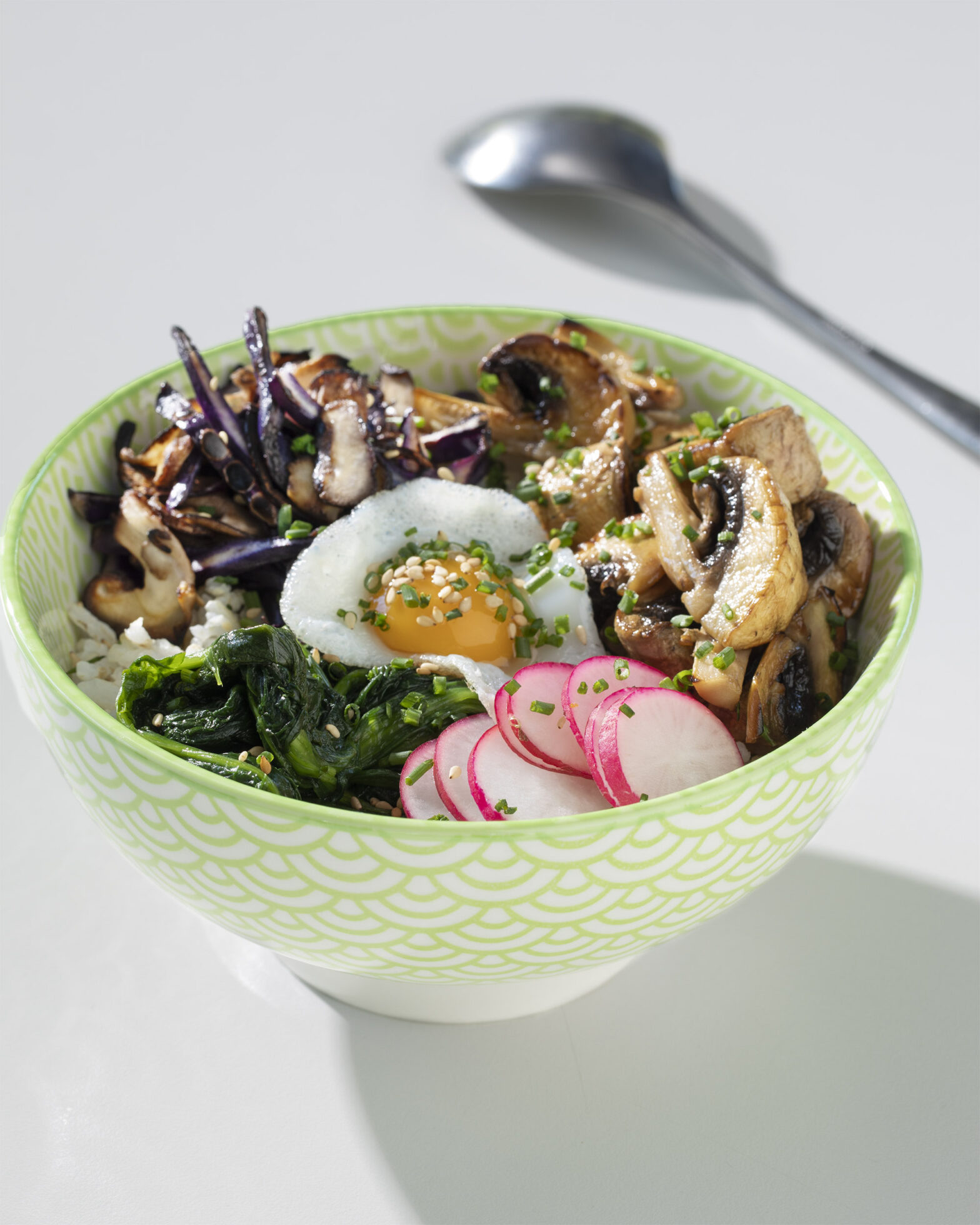
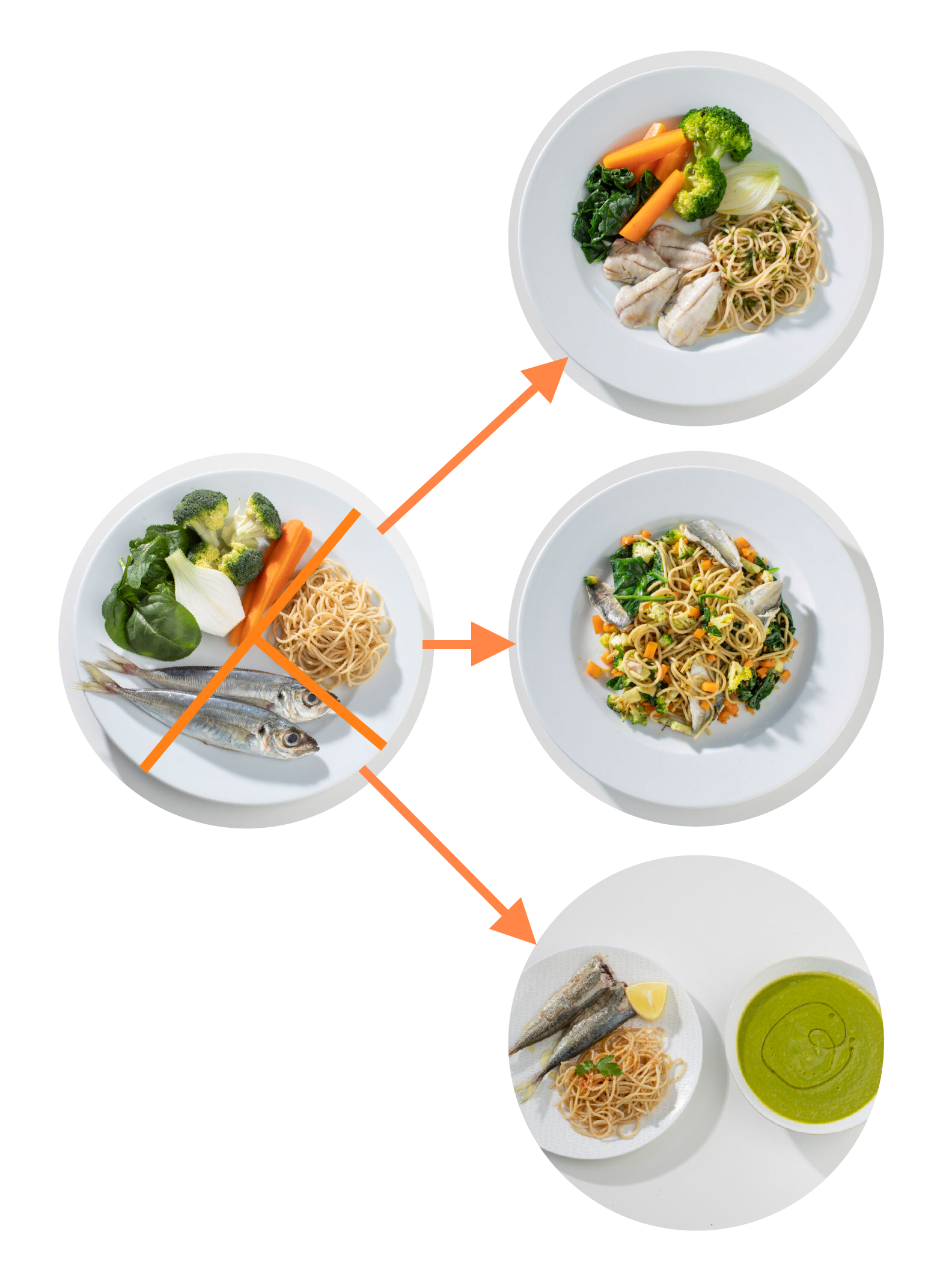
The plate method ensures having full meals and controls the energy intake in main meals. The plate method consists in dividing the plate into different sections: half of the plate should always contain vegetables, and the other half should contain whole grains and protein-based foods. With this method, you can prepare different types of dishes: single, combined, a first and second course, or a combination of small dishes.
You can include vegetables in many ways: salads, stews, purées, roasts, steamed, boiled, grilled or sautéed, or in other dishes, such as omelettes or soups. Mushrooms can be used as vegetables.
Potatoes, pasta, rice, or bread, among others, should be consumed in moderation and always by other food groups such as vegetables, mushrooms, fish, eggs… (See plate method above). Always choose wholemeal versions of starchy foods (if there are no contraindications).
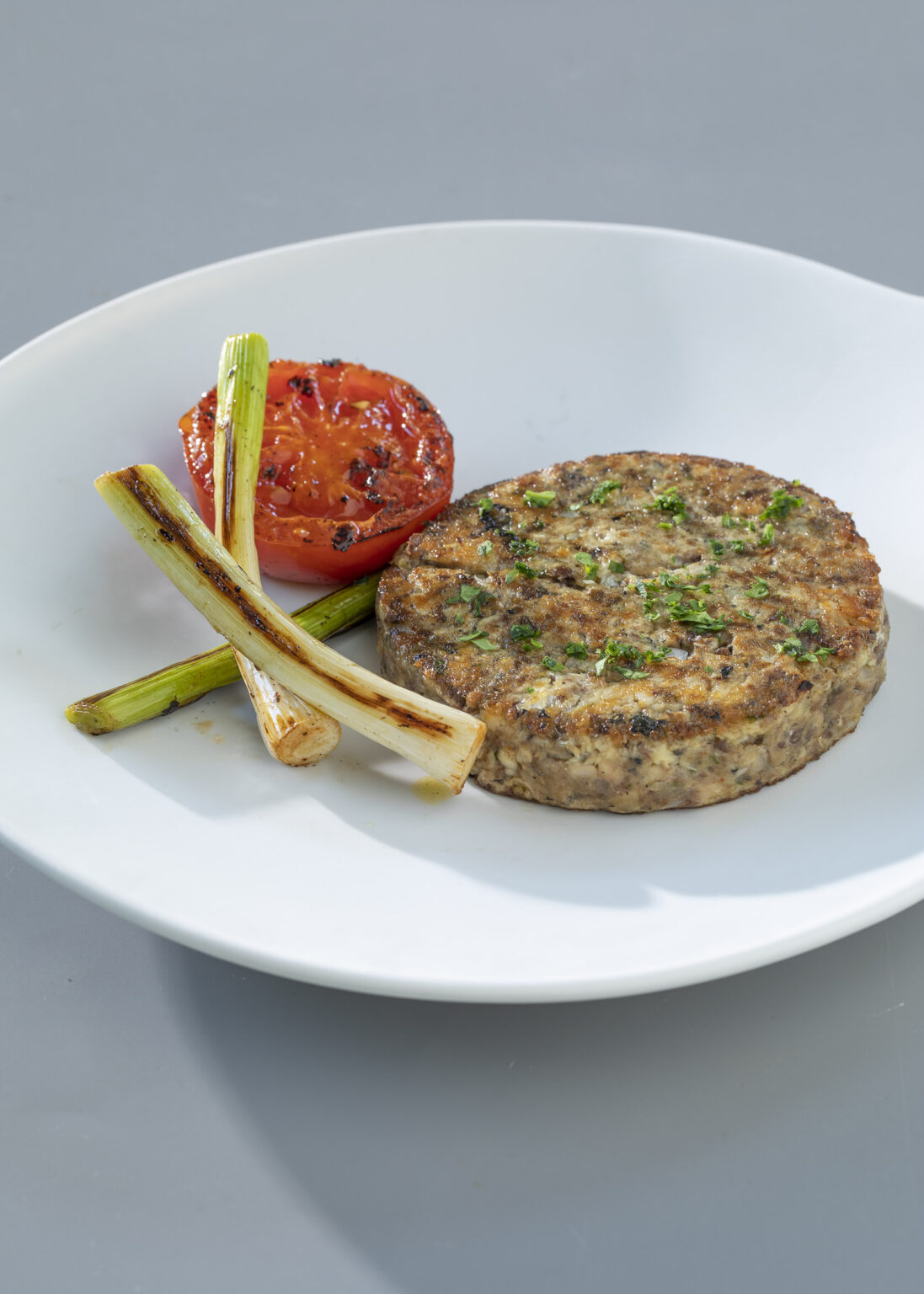
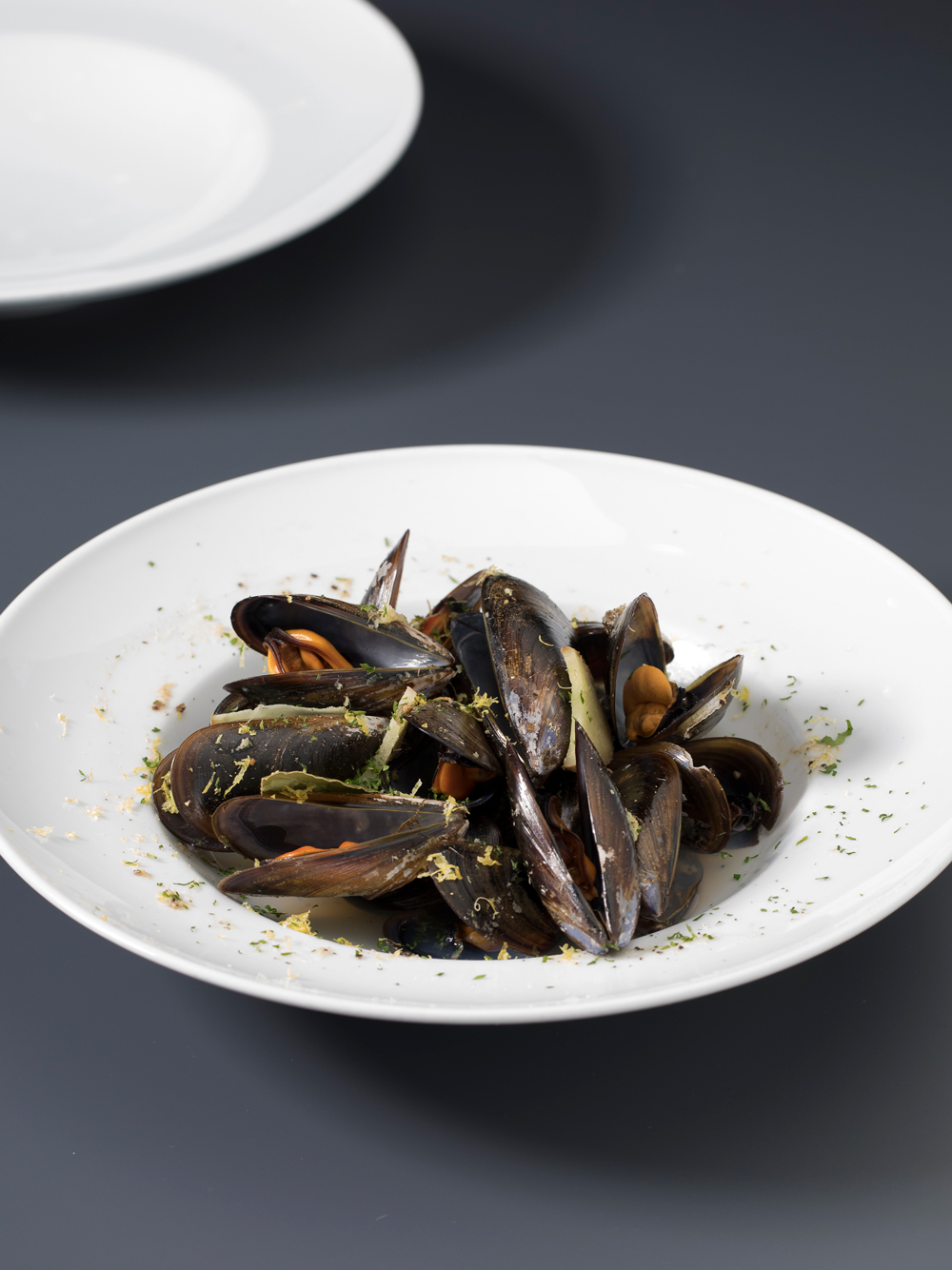
Eggs, fish, seafood, meat, pulses and derivatives, nuts, dried fruit… Always choose the leanest versions (limit consumption of fatty meats and cold meats) and cook with simple and low-fat methods: baked in the oven, grilled, microwaved, etc.
| Foods rich in protein | |
| Foods of animal origin |
|
| Foods of vegetable origin |
|
Three portions of fruit per day, limiting the consumption of juices and preferably having fruit as a dessert option.
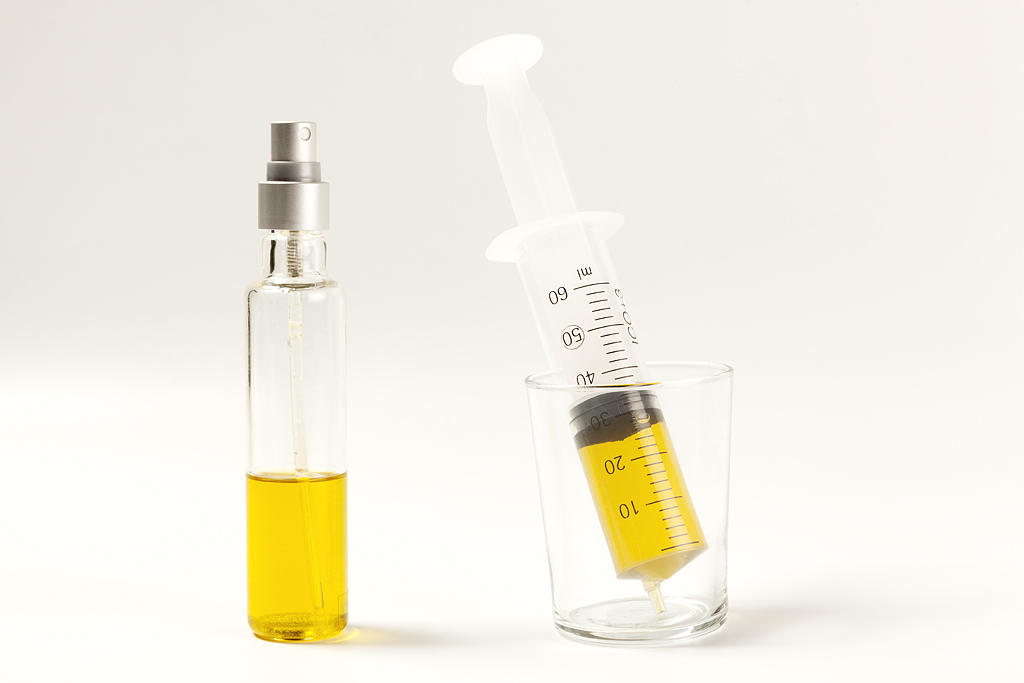
Do not use more than 3-4 tablespoons of olive oil per day (about 30-40 ml). Use a diffuser to pre-measure the amount of oil with the help of a syringe to help control and ration the recommended daily amount of oil.

Avoid keeping foods such as biscuits, chocolates, crisps, cold meats, juices, soft drinks, sweets, ice cream, etc. at home. If you have some of these foods at home, try to keep them out of sight, as having these types of food constantly visible places can lead to snacking between meals and eating larger quantities.
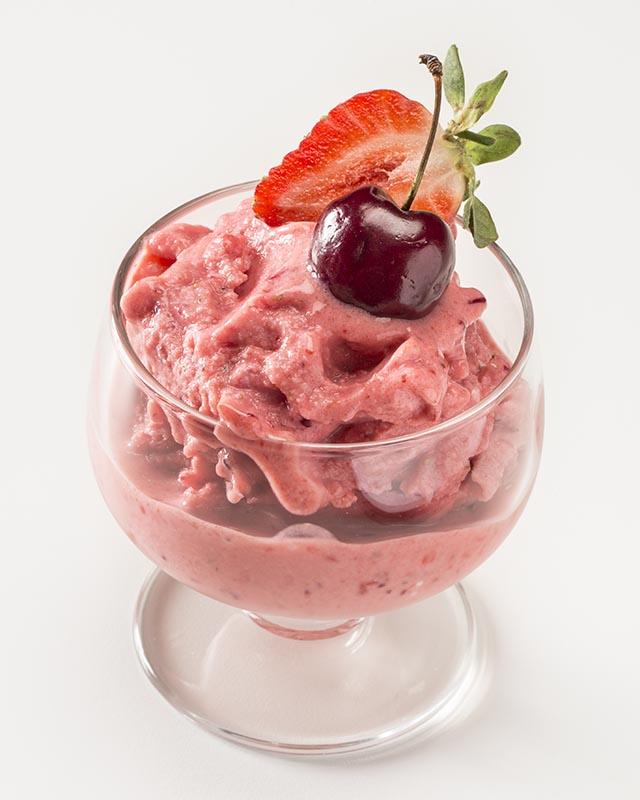
Replace with homemade ice cream recipes, sugar-free ice cream.
To avoid second servings, try not to bring the cooking pot or saucepan to the table.
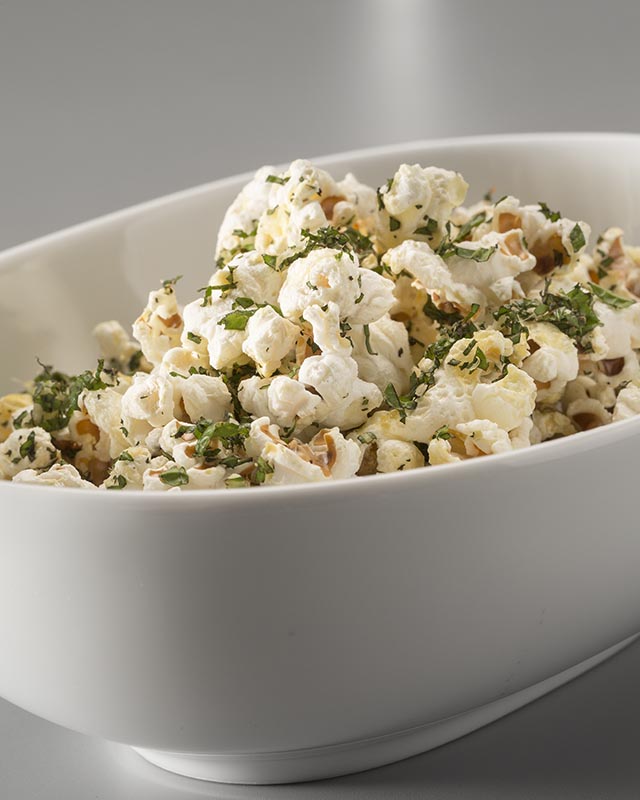
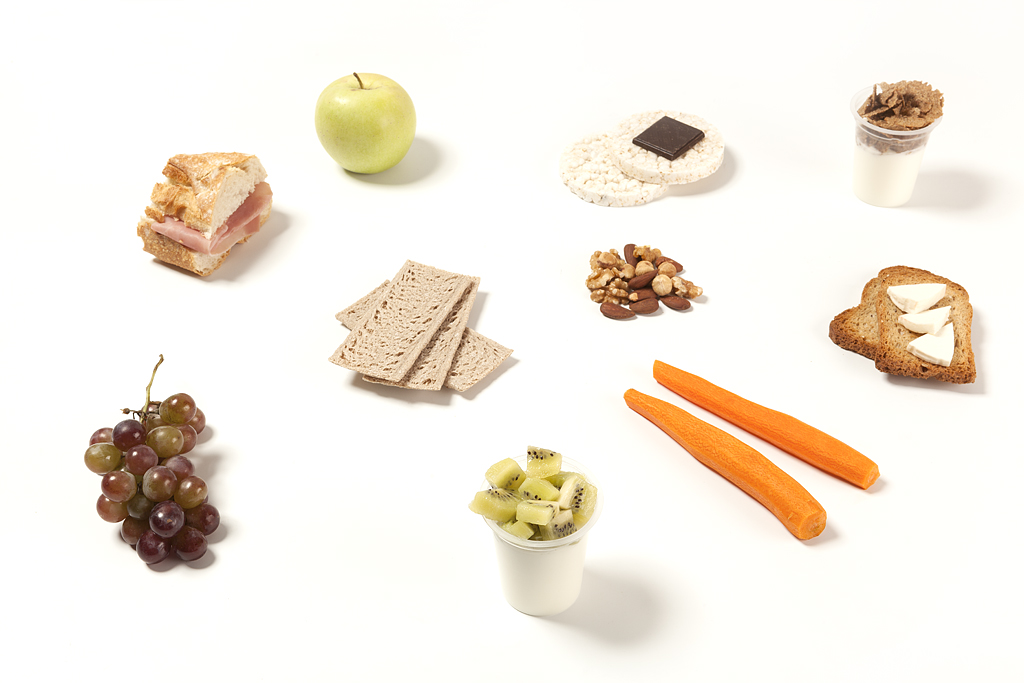
For the times when you feel the need to snack choose food as: fruit, carrots, herbal teas, low-fat homemade popcorn, whole-grain pancakes, low-fat yoghurt, etc., are good options.

Skimmed or semi-skimmed milk, low-fat or skimmed yoghurts (unsweetened), low-fat fresh or soft cheeses (such as ricotta).
Establishing regular mealtimes helps to regulate appetite.
To avoid overeating, eat calmly, without any distractions, or with family and friends.
Daily weighing can lead to demotivation and obsession with weight. Weigh yourself only once a week.















